Categories: Molecular Biology, Genetics, Biochemistry
Tags: start codons, protein synthesis, codons, translation, genetic code, mRNA, molecular biology
Introduction
In the intricate world of molecular biology, understanding the mechanisms of protein synthesis is crucial. At the forefront of this process are start codons, which play a vital role in initiating translation. This article will explore what start codons are, their importance in protein synthesis, and how they function within the genetic code.
What Are Start Codons?
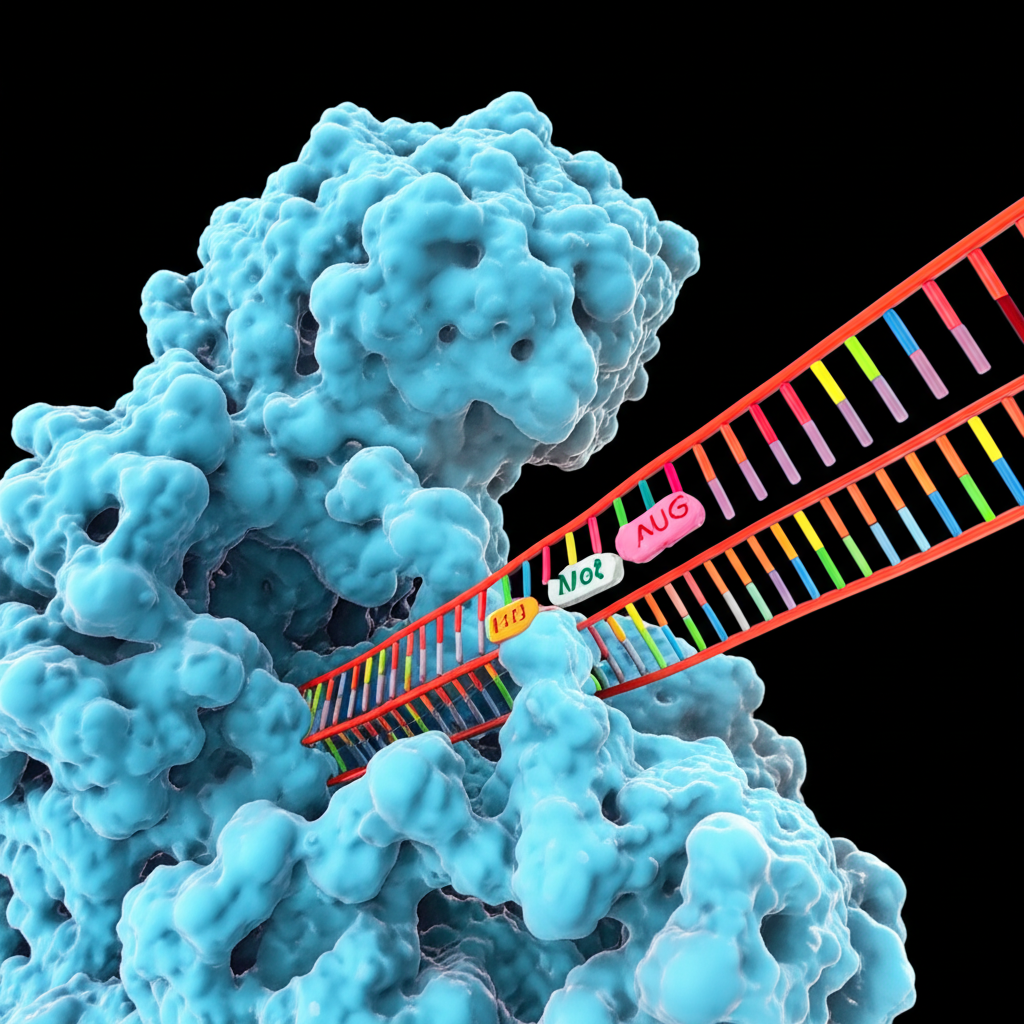
Start codons are specific sequences of nucleotides in messenger RNA (mRNA) that signal the beginning of translation. The ribosome reads these codons during protein synthesis, marking the point at which the assembly of amino acids into a polypeptide chain begins.
Key Features of Start Codons:
- Recognition by Ribosomes: Start codons are recognized by the ribosomal machinery, which facilitates the assembly of amino acids.
- Specific Sequence: The most common start codon is AUG, which codes for the amino acid methionine. This codon is crucial for the initiation of protein synthesis.
- Universality: While AUG is the primary start codon in eukaryotic and prokaryotic organisms, other codons like GUG and UUG can also serve as start codons under specific circumstances.
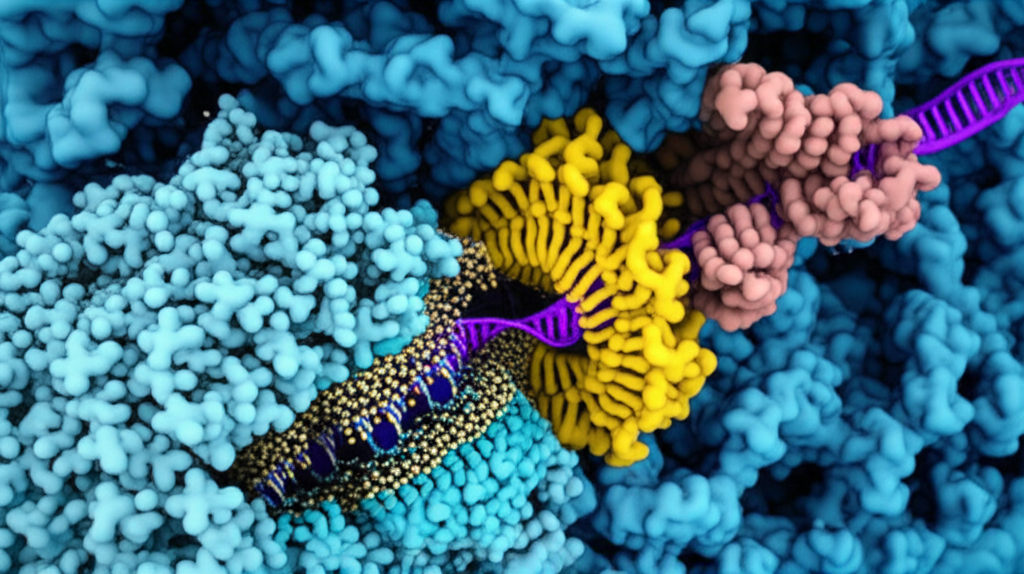
The Role of Start Codons in Protein Synthesis
The process of protein synthesis can be broadly divided into three key stages: initiation, elongation, and termination. Start codons are integral to the initiation phase.
Initiation Phase:
- Binding of mRNA: The mRNA strand binds to the ribosome, and the start codon (AUG) is aligned within the ribosome's active site.
- tRNA Recruitment: A transfer RNA (tRNA) molecule carrying methionine recognizes the start codon through complementary base pairing, allowing the ribosome to prepare for elongation.
- Formation of the Initiation Complex: The ribosome assembles the initiation complex, setting the stage for the elongation of the polypeptide chain.
Table: Common Start Codons
| Codon | Amino Acid | Organisms |
|---|---|---|
| AUG | Methionine | Eukaryotes, Prokaryotes |
| GUG | Valine (occasionally) | Some Prokaryotes |
| UUG | Leucine (occasionally) | Some Prokaryotes |
Importance of Start Codons
Start codons are essential for several reasons:
- Correct Protein Formation: They ensure that proteins are synthesized correctly, starting with the right amino acid sequence.
- Regulation of Gene Expression: The presence of a start codon affects the efficiency of translation, thus influencing gene expression levels.
- Evolutionary Significance: The universality of the start codon (AUG) across various organisms highlights its evolutionary importance in maintaining the fidelity of protein synthesis.
"Start codons are not just mere sequences; they are the gatekeepers of protein synthesis, determining the path of genetic information." – Dr. Jane Smith, Molecular Biologist
How Start Codons Function
Start codons interact with the ribosome and tRNA during the translation process. Here’s a simplified view of this interaction:
mRNA: ...AUG... (Start Codon)
|
v
Ribosome: [Ribosomal Complex]
|
v
tRNA: [Methionine tRNA]Common Questions About Start Codons
What happens if a start codon is missing?
- The ribosome will be unable to initiate translation, resulting in no protein synthesis.
Can there be multiple start codons in a single mRNA?
- Yes, mRNAs can contain multiple AUG codons, but only the first recognized AUG is typically used for initiation.
Do all organisms use AUG as a start codon?
- While AUG is the primary start codon, some prokaryotes can initiate translation with alternative codons like GUG and UUG.
Conclusion
Understanding start codons is crucial for grasping the fundamentals of protein synthesis and genetics. These essential sequences not only signal the beginning of translation but also play a pivotal role in ensuring that proteins are synthesized accurately and efficiently. As research in molecular biology progresses, the importance of start codons continues to be a focal point in understanding genetic expression and regulation.
Call-to-Action
Dive deeper into the world of molecular biology with our advanced resources. Explore our collection of articles on genetic code regulation and protein synthesis today!
Social Media Snippet: Unlock the secrets of molecular biology! Discover what start codons are and their crucial role in protein synthesis. Learn more in our latest blog post! #MolecularBiology #StartCodons
Suggested Internal Links:
Suggested External Links:
FAQs:
What is a start codon?
- A start codon is a specific mRNA sequence that signals the beginning of protein synthesis.
Why is AUG the most common start codon?
- AUG codes for methionine, which is the first amino acid in most protein sequences, making it essential for proper protein formation.
Can start codons vary between organisms?
- While AUG is the universal start codon, some prokaryotes can use alternative codons like GUG or UUG in certain conditions.